In the first half of this year, the financial industry is a hot spot for cybercriminals. The proliferation of personal data by online banking services is the “hot piece” for them. Understanding that, the following article will share about the top OWASP vulnerabilities today. And methods to help businesses keep their websites safe.
OWASP – Safe Website Security Project
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) is a non-profit organization that helps professionals protect websites from cyberattacks. OWASP currently has 32,000 volunteers worldwide. They are website security reviewers and researchers on cybersecurity threats. Outlining issues that the cybersecurity community needs to pay attention to.
The OWASP Top 10 is a list of the most important website security vulnerabilities. Of course, in fact, website security risks don’t just stop at 10. The OWASP Top 10 only shows the top risks that security experts need to pay attention to. So that they can promptly come up with mitigation plans and prevent them, keep the website safe.
OWASP assesses cyber-attack risks periodically. The assessments are based on the following four criteria: ease of exploitation, popularity, discoverability, and business impact. Based on that, they identified the 10 most severe attack risks.
Top website security risks OWASP
The financial industry becomes a hot spot for attacks in the first half of 2021. The top three OWASP attack risks by volume that have strongly impacted the financial services sector since early 2021 are data leaks, RCE/RFI, and Cross-site scripting (XSS).
Data leak
Data leak of type OWASP A3:2017-Sensitive data leak. The OWASP organization summarizes, “Many web applications and APIs do not properly protect sensitive data. Such as financial information, healthcare and PII. Attackers can steal or modify data with weak security. They then commit credit card fraud, identity theft or other criminal acts.”
Sensitive data can be compromised without additional safeguards. Like encrypting them at rest or in transit. And measures to protect them when communicating with other browsers are essential.
Injection
OWASP classifies RCE/RFI as A1:2017 - Injection. According to OWASP, “Website Injection vulnerabilities such as SQL, NoSQL, OS, and LDAP occur when untrusted data is sent to the interpreter as part of a command or query. The attacker’s hostile data can fool the interpreter. The interpreter then executes the unintended commands. Or unauthorized access to the data without permission.
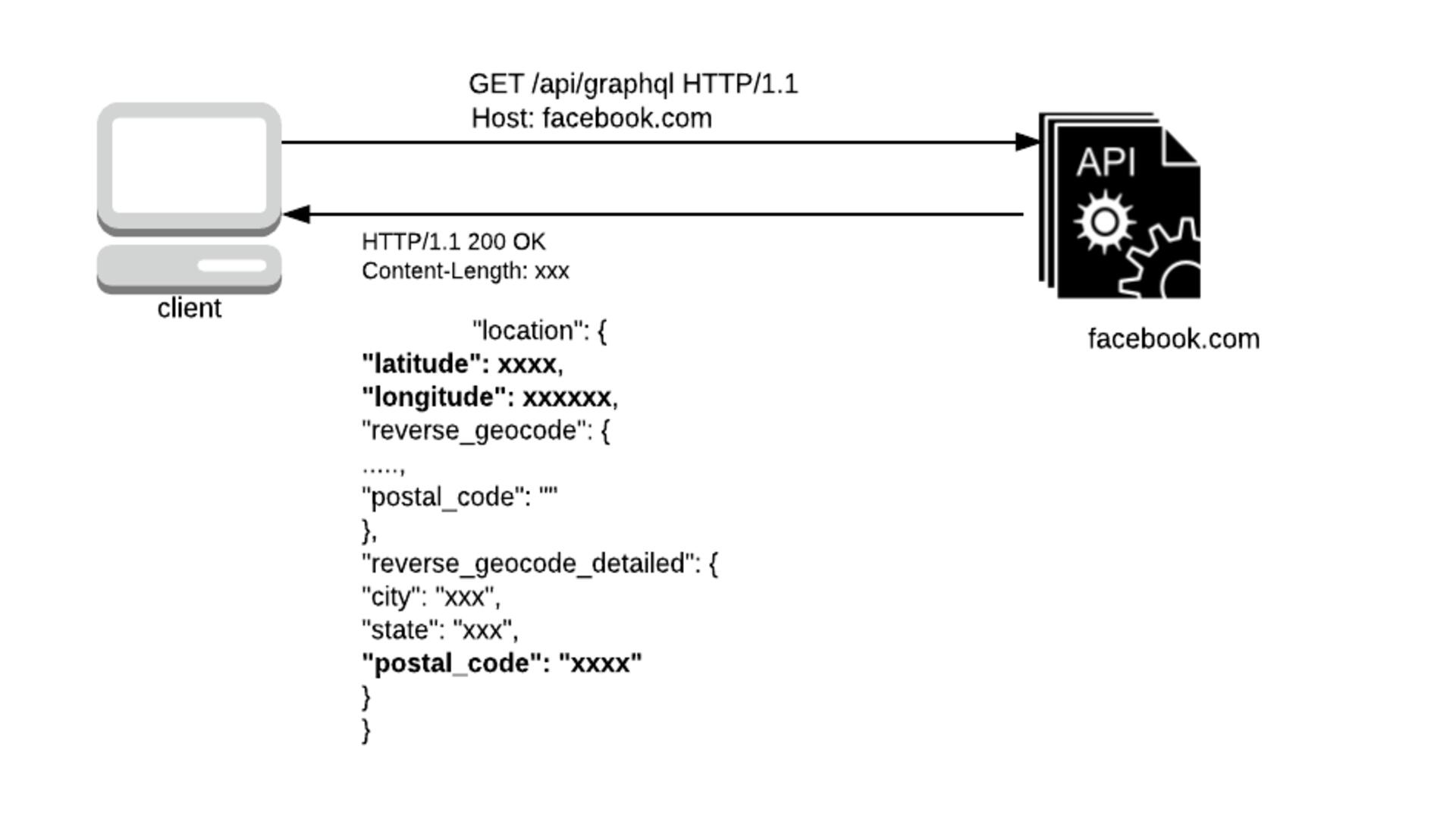
Injection
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) has its own risk category, A7:2017-Cross-Site Scripting XSS. OWASP explains, “The XSS error occurs when an untrusted application or data appears in a new web page without being authenticated. Or update an existing website with user-supplied data using the browser API to generate HTML or JavaScript. XSS allows attackers to execute scripts in the victim’s browser. They can hijack user sessions. Then break the surface of websites or redirect users to malicious sites.”

Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
Summary of the leading OWASP website security vulnerabilities in the financial sector
| Attack Name | OWASP Category | Percentage of Attacks | Principal risk to the financial services sector | | Data Leakage | A3:2017-Sensitive Data Exposure | 21,9% |
Data leakage enables attackers to steal or modify weakly protected yet high-value sensitive financial data, enabling them to commit credit card fraud, identity theft, or other crimes.
| | RCE / RFI | A1:2017-Injection | 20,5% |
For financial services especially, when remote attackers run malicious code on servers to exfiltrate data, the data is often sensitive personal data. Once exfiltrated using this method, attackers use it to commit credit card fraud, identity theft, etc.
| | Cross-Site Scripting | A7: 2017-Cross-Site Scripting XSS | 19,4% |
Cybercriminals inject client-side scripts into web pages viewed by other users. Because the malicious script is on the client-side, it is not attached to the targeted website but to unsuspecting website users. This presents a significant risk to the financial services industry because cybercriminals can use this method to extract valuable information (e.g., session cookies) that can be used to take over customers’ accounts on financial services sites.
| | | |
The level of website security risk of the financial services industry
The number of attack-type incidents in the financial industry is largely the same as in other industries. But the XSS incident of this industry alone is nearly 8% higher than that of other industries. It may be due to the increased number of online banking users since 2020.
The epidemic situation has promoted the strong development of online banking services. According to analysis by Fidelity National Information Services, in April 2020, the number of registrations for mobile banking services increased by 200%. That increase resulted in a 50% drop in bank traffic in the same month, according to US banking data firm Novantas.
Data leaks are the most prevalent type of website security risk in financial services with 22%. Again, the cause could be an increase in the number of online banking users. They use these services to manage their finances. Because of the huge value of such data, financial institutions become targets of cybercriminals.
How to keep the website safe?
To prevent the leakage of sensitive personal data, you should consider:
-
Identify sensitive data and implement appropriate security controls.
-
Do not store sensitive data unless absolutely necessary. Remove or encrypt them.
-
Encrypt all sensitive data even when they are at rest using strong encryption algorithms, protocols and keys.
-
Encrypt data even in transit using secure protocols such as TLS and HTTP HSTS.
-
Disable caching for sensitive data.
-
Store passwords using strong hash functions like Argon2, scrypt, and bcrypt.
To mitigate injection attacks, VNETWORK recommends:
-
Use secure API to avoid using interpreter
-
Use active server-side input validation or “whitelist”
-
Escape special characters
-
Use LIMIT and other SQL controls in queries to avoid revealing records in case of SQL inserts.
VNIS – The ultimate website security solution
-
Cloud WAF Firewall: will filter all malicious requests and prevent Layer 7 DDoS attacks and protect websites from OWASP’s top 10 security vulnerabilities.
-
Multi CDN: combines many of the world’s leading CDN providers such as Akamai, Cloudflare, AWS… with more than 2,300 PoPs and 2,600 Tbps capacity from all CDN partners. Therefore, when any CDN provider has a problem, there will be another CDN to replace. In addition, Multi CDN also protects Layer 3/4 from DDoS attacks traffic up to Tbps.
-
AI (artificial intelligence) load balancing: helps monitor website performance in real time. Load balancing traffic when there is a sudden fluctuation in traffic.
If you want to register for a comprehensive website security service trial, please leave your contact information below or call the hotline: (028) 7306 8789 for further advice.
VNIS - Stop worrying about website security for businesses
