VNETWORK is proud that VNCDN’s CDN (Content Delivery Network) system can support HTTP/3 technology well. We are ready for the journey of helping your web server deliver data at maximum speed with this technology. Therefore, in the article below, we will talk about the development journey and benefits of HTTP/3 technology, and finally, how businesses can integrate this technology into the server system.
HTTP/3 is widely used in the internet environment
HTTP/3 - The new protocol that supports fast data transmission on the internet has been applied in most web browsers. HTTP/3 has satisfied most users once they use it through browsers that support this protocol.
In order to follow the trend and match the user’s desire for maximum-speed browsing, a series of web browsers have applied HTTP/3 technology to win the most favor of users around the world.
In addition, web servers must also configure this HTTP/3 protocol to be integrated into the system to ensure that the transmission process from the web server to the browser is achieved at the highest speed.
The process of integrating HTTP/3 into a web server is quite complicated, except that the web server has a built-in CDN technology that supports HTTP/3, they don’t have to do anything, because a CDN that supports HTTP/3 has solved the problem. This protocol compatibility story goes from the web server to the web browser, giving users super-fast content access results.
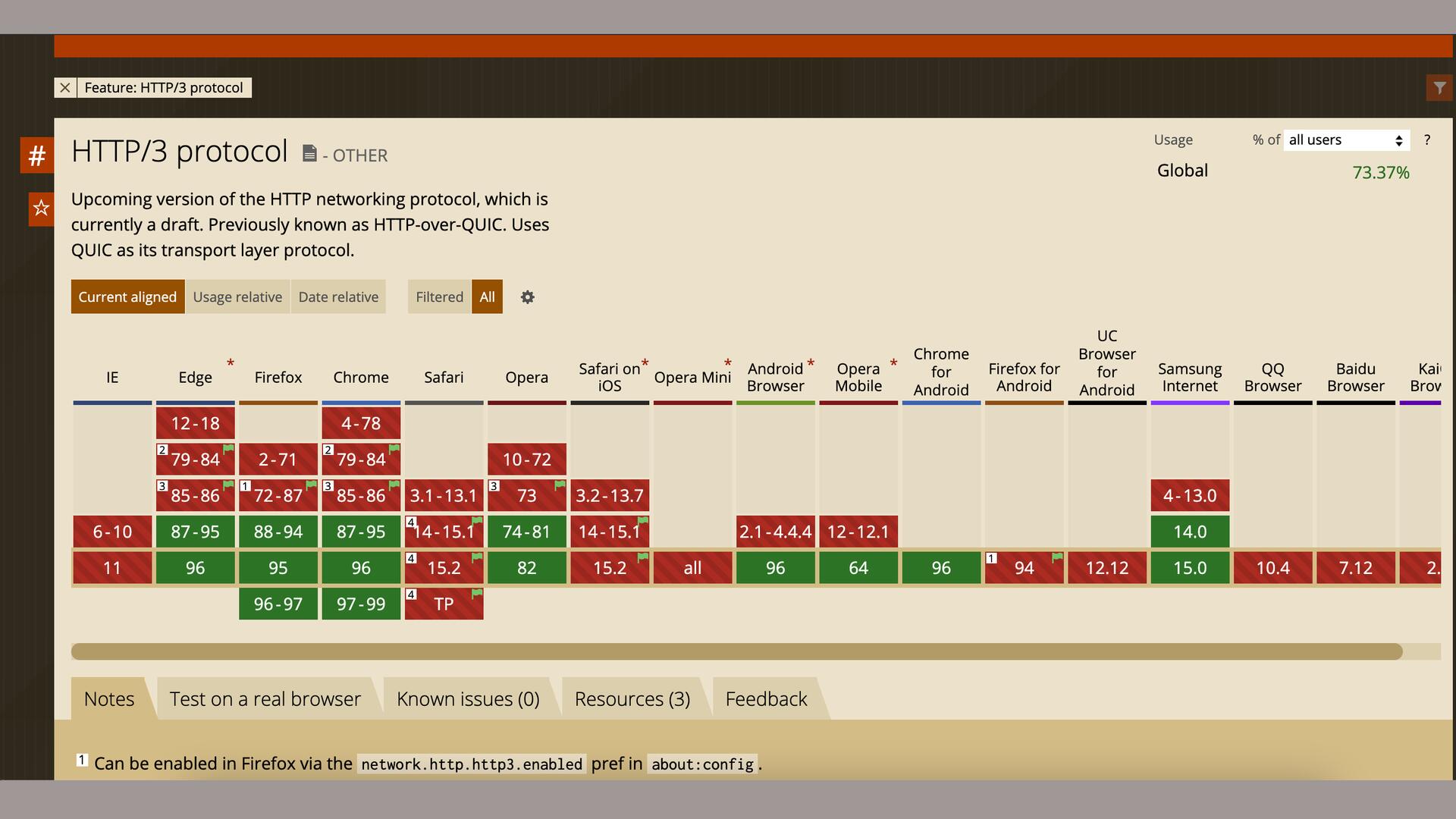
Most web browsers have adopted HTTP/3 technology
VNETWORK is the first CDN provider in Vietnam to officially support HTTP/3
As announced on December 15, 2021, VNETWORK’s CDN system officially supports HTTP/3. This is the new standard for the web, providing fast, reliable and secure connections to websites or APIs.
Once the HTTP/3 CDN is enabled for your domain, customers can interact with websites and APIs using the world’s most popular HTTP/3 protocol.
With CDN technology supporting HTTP/3, VNETWORK has now been able to bring the best performance to websites, as well as solve the backlog in HTTP/2 technology.
Next, we will begin to learn about the history and development of this protocol.
The process of formation and development of the HTTP protocol
Standards innovation on the Internet has been difficult in the past because of the choice of server or client preference. Because both sides of the connection need to support a new communication protocol.
In the past, VNETWORK’s CDN has supported HTTP/2, and TLS 1.3, to encrypt SNI. And now, we’ve been working to promote better transport standards by working with relevant organizations to build a better Internet platform with HTTP/3’s protocol.
During the development of the HTTP/3 standard, we worked closely with industry partners to make it possible to use the HTTP/3 protocol in conjunction with the best CDN system.
Enterprises widely deploying HTTP/3 CDN will make the user’s web experience much better.
Why do businesses need to apply HTTP/3 technology?
Before diving deeper into HTTP/3, let’s review the evolution of HTTP over the years to better understand why HTTP/3 is so important and necessary.
In 1996 when the HTTP/1.0 specification defined the basic HTTP text string format. With the HTTP/1.0 protocol, a new TCP connection is created for each request or response exchange between the client and the server, all requests incur a delay as the TCP handshake and TLS is completed before each request.
Instead of sending all remaining data as quickly as possible after a connection is established, TCP enforces a phase called “slow start”, which helps control congestion in the TCP protocol. At any point in time, if there is traffic congestion, it can flood the network with packets that cannot be handled in time. New connections are forced to wait for the session, they cannot use all available network bandwidth immediately.
The HTTP/1.1 revision solved these problems with better connections, allowing customers to reuse TCP connections and save on initial connection setup costs, reducing delays when there are many requests. demand at the same time.
While multiple requests can share the same connection, they must still be serialized one after the other, so that the client and server can only perform a single request or response exchange at any given time. points for each connection.
As the web grows, browsers need more concurrency when fetching and rendering web pages because the number of resources (like CSS, JavaScript, images, etc.) from the number of websites increases over the years. But since HTTP/1.1 only allows the client to do one HTTP request or response exchange at a time, the only way to achieve concurrency at the network layer is to use multiple TCP connections to the same machine in parallel. origin, thereby causing the loss of most of the benefits to active connections.
And after more than a decade came the HTTP/2 technology, which implemented HTTP and simultaneously multiplexed different HTTP exchanges on the same TCP connection, helping the browser to reuse TCP connections efficiently. more fruitful.
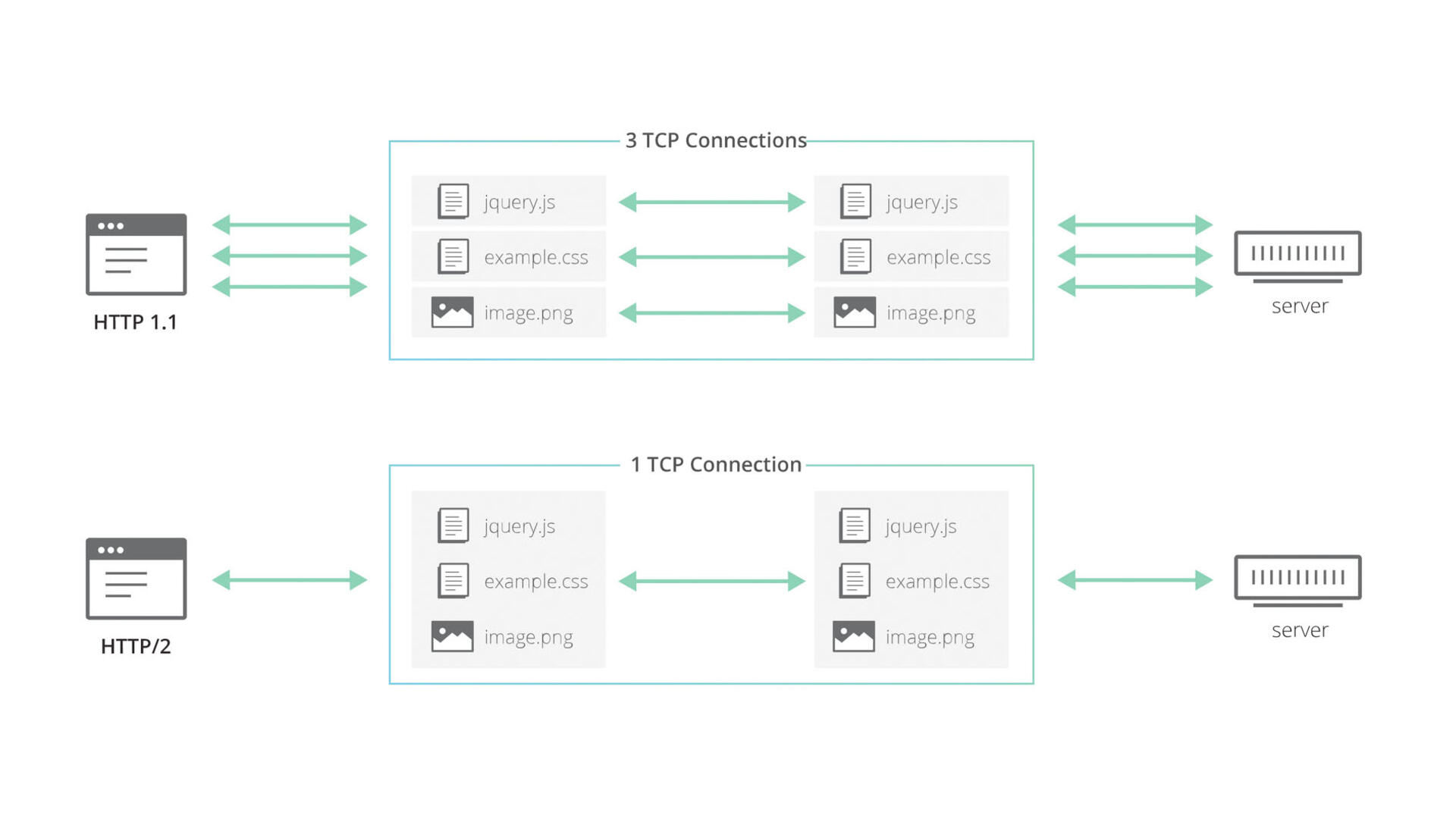
HTTP/2 makes it more efficient for browsers to reuse TCP connections
But, HTTP/2 still can’t solve the original problem, which is inefficient use with a single TCP connection - as multiple requests or responses can be passed over the same connection, within the same connection. a time. However, all requests and responses are equally affected by packet loss (when something goes wrong), even if the data loss is related to only a single request. When the HTTP/2 layer can separate different HTTP exchanges on separate streams. The TCP protocol does not solve this problem and as a result, a stream of bytes with no meaning is generated.
TCP’s role is to deliver the entire stream in the correct order, from one endpoint to another. When a TCP packet carries some lost bytes on the network path, it creates a gap in the stream and TCP needs to fill it by resending that lost packet. And as a result, no bytes have been successfully sent since the lost bytes. Therefore, this sending process will be delayed because applications will not be able to process when the packet is missing bits.
How has HTTP/3 changed the world?
This is where HTTP/3 comes into play: instead of using TCP as the transport layer for the session, it uses QUIC, a new Internet transport protocol. QUIC threads share the same QUIC connection, so no handshake and a slow start to create new. QUIC streams are distributed independently so that in most cases packet loss affects only one stream and not the others. This is possible because QUIC packets are encapsulated on top of UDP datagrams.
Using UDP is much more flexible than TCP and helps make QUIC appear in userspace - updates to protocol implementations are not tied to operating system updates as is the case with TCP.
With QUIC, HTTP streams can simply be mapped on top of QUIC streams to get all the benefits of HTTP/2 without blocking.
QUIC also combines the 3-way TCP handshake with the TLS 1.3 handshake. Combining these steps makes encryption and authentication provided by default, and also helps establish a connection faster.

HTTP/3 uses QUIC, a new Internet transport protocol
Why not use HTTP/2 over QUIC?
After all, HTTP/2 also provides multiplexing. It is somewhat more complicated, although it is true that some HTTP/2 features can be mapped onto QUIC very easily, most cannot. In particular, HTTP/2’s header compression called HPACK depends a lot on the order in which different HTTP requests and responses are sent to the endpoints. QUIC enforces byte distribution in single streams but does not guarantee sorting between different streams.
It requires creating a new HTTP header compression scheme, called QPACK, which can fix the problem but forces changes to the HTTP mapping. In addition, some of the features supported by HTTP/2 (such as flow control) are also provided by QUIC, so they were dropped from HTTP/3 to remove unnecessary complexity.
HTTP/3 will usher in a new era

HTTP/3 has opened a new era
QUIC and HTTP/3 are standards that promise to address many of the shortcomings of previous standards and usher in a new era of performance on the web. So, how do we effectively implement this new technology?
How can businesses apply HTTP/3 technology?
HTTP/3 makes the web experience faster, more reliable, and more secure for all users. In order for the protocols to be used safely and optimally, you will need a good development and operations team to correctly execute this HTTP/3 transition.
Or you can ask a CDN company that supports HTTP/3 to set up and configure the protocols for you. In addition, using a CDN is the most effective way to speed up your website trusted by leading businesses.
Using CDN is one of the ways to optimize website performance
You can register to experience VNCDN HTTP/3 CDN service at the form below or call the quick support hotline: (028) 7306 8789.
