What is Phishing?
Phishing is a common cyberattack technique designed to steal sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, one time passcodes, and financial data. Attackers impersonate trusted entities such as banks, service providers, or internal administrators to trick users into disclosing credentials or accessing malicious links.
Stolen credentials and exploited vulnerabilities often become entry points for more complex attacks, including ransomware, Business Email Compromise and Advanced Persistent Threat campaigns.

See also: How to protect enterprise email systems
Why businesses are prime targets for phishing
Phishing campaigns overwhelmingly target organizations rather than individual consumers. In digital operating environments, enterprises manage valuable data, large financial flows, and interconnected systems. Compromising a single internal account can allow attackers to expand access and exploit multiple critical resources. The following factors make businesses particularly attractive targets.
- Heavy reliance on email in operational workflows: Email is used for payment approvals, contract execution, partner communications, and internal coordination. Once an email account is compromised, attackers can initiate fraudulent transfer requests or distribute malware without raising immediate suspicion.
- High financial value and centralized approval authority: Finance departments and senior executives often have authority to process high value transactions. Business Email Compromise attacks can result in losses of hundreds of thousands of dollars from a single fraudulent transfer.
- Sensitive data concentrated on cloud platforms: Organizations increasingly store data on Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, and other SaaS platforms. A single compromised credential may expose internal documents, customer records, and administrative systems.
- Distributed work environments and remote access: Hybrid and remote work models require employees to access systems from multiple devices and networks. This expands the attack surface and complicates access control management.
- Uneven security awareness across departments: Not all employees receive comprehensive security training. A single lapse in judgment can serve as the starting point for a large scale compromise.
- Supply chain attacks: Attackers may compromise smaller organizations to use them as stepping stones toward larger partners. As a result, phishing poses risks not only internally but across the broader business ecosystem.
The typical phishing attack lifecycle
Although phishing can take many forms, most campaigns follow a calculated sequence of actions. Attackers do not simply send a single deceptive message. Instead, they develop structured campaigns that progress from reconnaissance to exploitation and privilege expansion. Understanding this lifecycle enables organizations to detect anomalies early and reduce potential damage.
Below are the five typical steps in a standard phishing attack lifecycle:
- Step 1 – Target reconnaissance: Attackers conduct reconnaissance to gather information about the organization’s structure, personnel roles, approval workflows, and business partners through corporate websites, social media profiles, or leaked data sources.
- Step 2 – Crafting the attack scenario: Based on the collected information, attackers create highly convincing fraudulent content, often leveraging urgency, executive pressure, or work related context to increase credibility.
- Step 3 – Inducing user action: The victim is prompted to provide login credentials, verify an account, or approve a transaction under the guise of routine business activity.
- Step 4 – Exploiting initial access: Once credentials or access rights are obtained, attackers silently infiltrate systems, monitor internal email communications, and gather additional sensitive data.
- Step 5 – Expansion and impact: Attackers execute financial fraud, exfiltrate data, or encrypt systems for ransom, with organizations often discovering the breach only after significant damage has occurred.

Common types of phishing attacks
Phishing does not exist in a single form. Depending on the target and context, attackers adjust their approach to maximize success and bypass traditional security controls. From mass email campaigns to highly targeted operations, each method presents different levels of risk to enterprises.
Spear phishing
Spear phishing is a targeted attack directed at a specific individual or department within an organization. Unlike broad distribution campaigns, spear phishing is built upon detailed research about the target.
Attackers may gather information from corporate websites, LinkedIn profiles, press releases, or previously leaked communications. The primary risk lies in its high level of personalization. Messages often reference active projects, partner names, internal titles, or operational details. When content aligns with real business activities, it becomes difficult to detect anomalies.
In enterprise environments, spear phishing frequently targets:
- Finance and accounting teams
- Contract management personnel
- IT administrators
- Mid level managers with approval authority
A request to confirm urgent payment to a partner or update internal system credentials, if properly contextualized, can bypass both user skepticism and basic email filters.
The consequences extend beyond password exposure. Once internal access is obtained, attackers can monitor communication flows, gather additional data, and prepare larger scale fraud or malware deployment campaigns. For this reason, spear phishing often serves as the entry point for organized cyber operations.
Phishing email
Phishing email remains the most common form of phishing and accounts for a significant portion of enterprise security incidents. Unlike spear phishing, it is typically conducted at scale and targets multiple users simultaneously.
Attackers distribute bulk emails impersonating common business scenarios such as:
- Account suspension alerts
- Unpaid invoices
- Security update notifications
- Delivery or refund confirmations
Although early campaigns were easier to detect, modern phishing emails increasingly leverage artificial intelligence to generate natural language, professional layouts, and convincing branding elements.
The enterprise risk extends beyond a single compromised user. If an employee clicks a malicious link and submits credentials, attackers can access internal mailboxes, analyze historical communications, send further fraudulent messages from the compromised account, and propagate malware across departments.
This internal amplification effect can rapidly escalate a localized incident into a full scale organizational crisis. Given email’s central role in business operations, phishing email continues to represent one of the most persistent and complex threats.

Whaling
Whaling is an advanced form of spear phishing that targets senior executives such as CEOs, CFOs, or financial directors. Instead of exploiting volume, attackers focus on individuals with authority over high value transactions or strategic information.
Messages often involve contracts, mergers and acquisitions, international transactions, or urgent transfer requests. Because the target audience consists of leadership roles, emails are carefully crafted with formal tone and contextual accuracy.
A single incorrect executive decision can lead to significant financial loss or exposure of confidential data. Whaling is therefore considered one of the highest risk phishing variants for enterprises.
Smishing
Smishing refers to phishing delivered via SMS messages. It exploits widespread mobile device usage and typically contains urgent messages related to banking accounts, suspicious transactions, or delivery notifications.
Because mobile interfaces shorten URLs and users rarely inspect full domain details, the likelihood of accessing fraudulent pages increases. In enterprise contexts, if employees use personal devices to access work accounts, smishing can become an initial access vector. The growth of mobile banking and remote work continues to increase smishing risk.
Vishing
Vishing involves phishing conducted through voice calls. Attackers may impersonate banks, government agencies, or internal executives to request sensitive information or transaction approval.
Direct verbal interaction reduces skepticism, especially when authority is implied. Advances in AI based voice cloning technology further increase the credibility of such attacks. Within enterprises, vishing may support targeted spear phishing campaigns or credential harvesting efforts.
Quishing
Quishing exploits QR codes to redirect users to fraudulent websites. This method commonly appears on electronic invoices, event materials, or public notices.
Because users cannot visually inspect the destination URL before scanning, verifying authenticity becomes more challenging. When combined with familiar login interfaces, quishing can capture credentials without raising suspicion.

Clone phishing
Clone phishing occurs when attackers replicate a legitimate email previously sent to a victim, then replace links or attachments with malicious content before resending it.
Because the message appears familiar and contextually relevant, recipients often perceive it as a routine update or reissued document. In environments with frequent internal communication, clone phishing can bypass initial suspicion and spread rapidly.
Pharming
Pharming operates at the infrastructure level by manipulating Domain Name System resolution to redirect users to fraudulent websites, even when correct URLs are entered.
Unlike other phishing techniques that rely heavily on user interaction, pharming exploits network layer weaknesses. Detection is difficult without robust infrastructure level protections. For enterprises, pharming can result in large scale credential harvesting if authentication and monitoring mechanisms are insufficient.
How to prevent phishing attacks
Phishing cannot be eliminated with a single tool. Because it combines human manipulation with evolving technical techniques, organizations must adopt a layered defense strategy that integrates technology, processes, and internal awareness. The objective is not only to block malicious messages but also to reduce impact when incidents occur.
Strengthening employee awareness and training
Humans remain the most targeted component in phishing campaigns. Regular security awareness training forms the foundation of defense. Employees should learn to recognize unusual urgency, sudden payment process changes, and unsolicited requests for sensitive information.
Internal phishing simulations help assess vigilance and improve response reflexes. However, training alone cannot eliminate human error. Technical controls remain essential.
Implementing authentication and account protection mechanisms
Configuring SPF, DKIM and DMARC reduces domain spoofing risks and protects brand integrity. These authentication standards form a critical defensive layer against impersonation.
Multi factor authentication should be enforced across all system access points. Even if credentials are compromised, MFA introduces an additional barrier against unauthorized access.
Monitoring and behavioral analysis
Modern security solutions go beyond static blocklists and signature detection. They analyze user behavior and risk levels associated with each session.
Detecting anomalies such as logins from unfamiliar geolocations, sudden device changes, or abnormal data access volumes enables early intervention. Continuous monitoring through a Security Operations Center further enhances incident detection and response.
Securing the email layer
Because most phishing campaigns originate from email, deploying advanced email security platforms is essential.
Capabilities should include:
- Real time content and link analysis
- Zero day malware detection
- Lookalike domain identification
- Prevention of internal propagation
Dedicated solutions intercept threats before they reach user inboxes, reducing reliance on individual vigilance.
Establishing a clear incident response process
Even with multiple defensive layers, organizations must prepare response playbooks. Rapid response significantly influences overall impact.
Upon detecting suspicious activity, compromised accounts or devices should be isolated immediately. Security and IT teams must be notified without delay.
Following containment, organizations should assess impact scope, rotate credentials, enforce stronger authentication, and review access logs. A well defined incident response framework not only minimizes losses but strengthens long term resilience against sophisticated phishing campaigns.
EG Platform multi layer email security solution against phishing
In most phishing campaigns, email serves as the initial entry point. However, many modern attacks no longer rely on obvious malware. Instead, they exploit psychology and contextual relevance, making traditional filters insufficient.
EG Platform by VNETWORK is the only global email security platform fully compliant with the ITU T X.1236 standard defined by the International Telecommunication Union. The solution leverages AI and Machine Learning to provide comprehensive bidirectional email protection, covering both inbound and outbound traffic to prevent phishing, social engineering and targeted attacks.
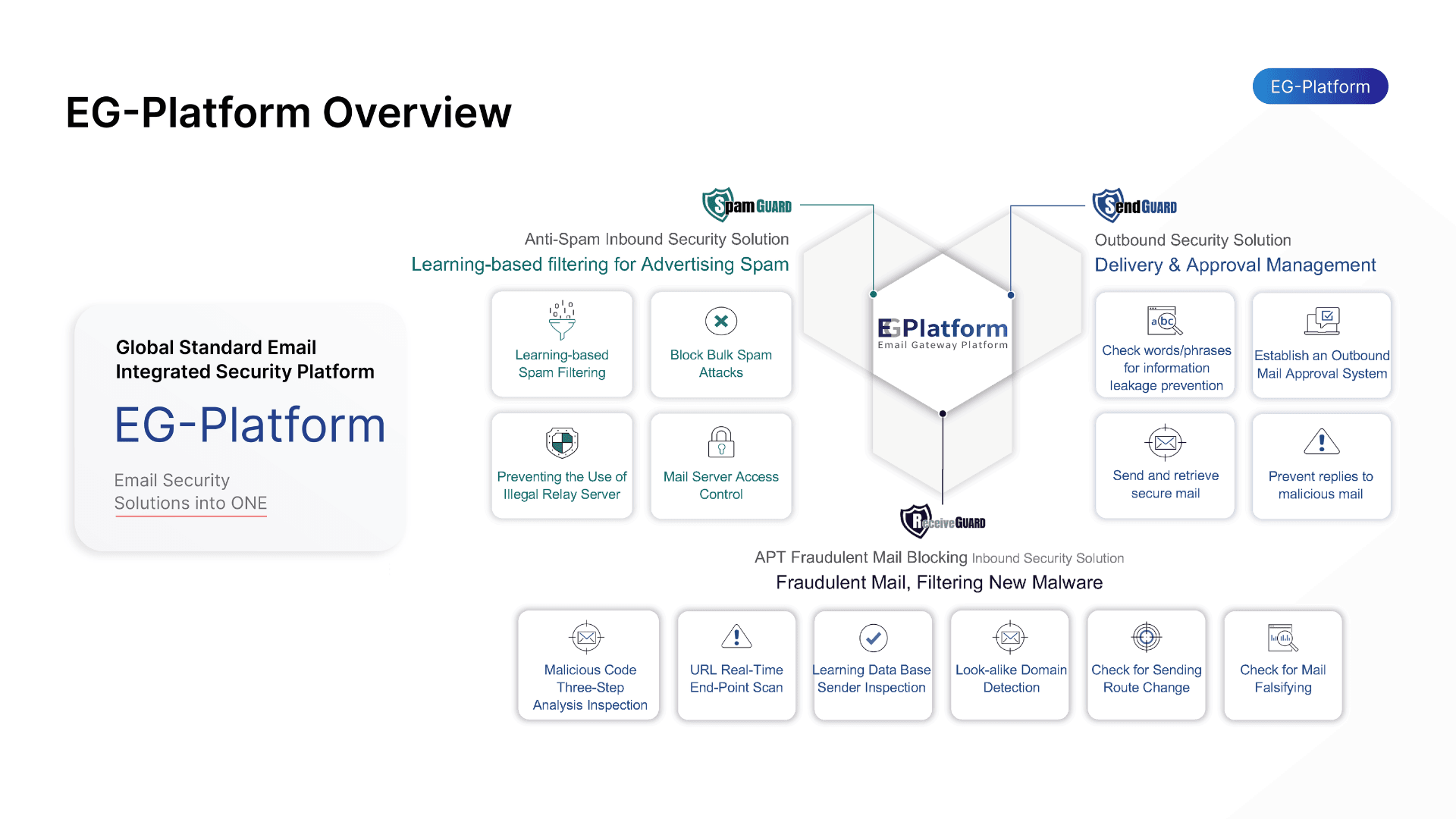
The system is built on a three layer protection model.
- Spam Guard applies Machine Learning and Bayesian filtering to score email risk while validating SPF, DKIM, and DMARC standards to detect domain spoofing. It blocks spam, phishing messages and malware at early stages.
- Receive Guard protects inbound email by analyzing content, attachments, and URLs within a virtual sandbox environment. It evaluates IP reputation, header anomalies, and behavioral indicators to detect impersonation attempts. Suspicious links can be neutralized before users access them.
- Send Guard monitors outbound email to prevent compromised internal accounts from distributing phishing or leaking sensitive data. IP and geographic filtering combined with keyword inspection reduces incident propagation risk.
Through its multilayer architecture and AI driven behavioral analytics, EG Platform enables enterprises to detect and stop sophisticated phishing campaigns before they result in financial damage or reputational harm.
FAQ about phishing and email security
1. Is phishing a virus?
No. Phishing is a deception technique designed to steal information or induce harmful actions. However, phishing often serves as the entry point for malware distribution, ransomware deployment, or system intrusion.
2. Are small businesses targeted by phishing?
Yes. Attackers do not exclusively target large enterprises. Small and medium businesses often lack dedicated security teams and may serve as supply chain entry points.
3. Why is phishing becoming harder to detect?
Modern phishing campaigns use AI to generate natural language content, personalize messaging, and replicate familiar communication styles. Many emails contain no obvious malware or suspicious links.
4. Are SPF, DKIM, and DMARC sufficient protection?
These standards help prevent domain spoofing but cannot fully eliminate phishing. Attackers may use alternative domains or compromised legitimate accounts. Behavioral analysis and bidirectional protection remain necessary.
5. How can phishing emails be identified?
Common indicators include unusual urgency, unexpected payment process changes, minor domain inconsistencies, or content misaligned with business context. Highly targeted spear phishing campaigns may still appear legitimate.
6. What should be done if an employee clicks a phishing email?
Immediately disable the affected account, rotate credentials, revoke active sessions, and review access logs to assess scope. Activate incident response procedures as required.